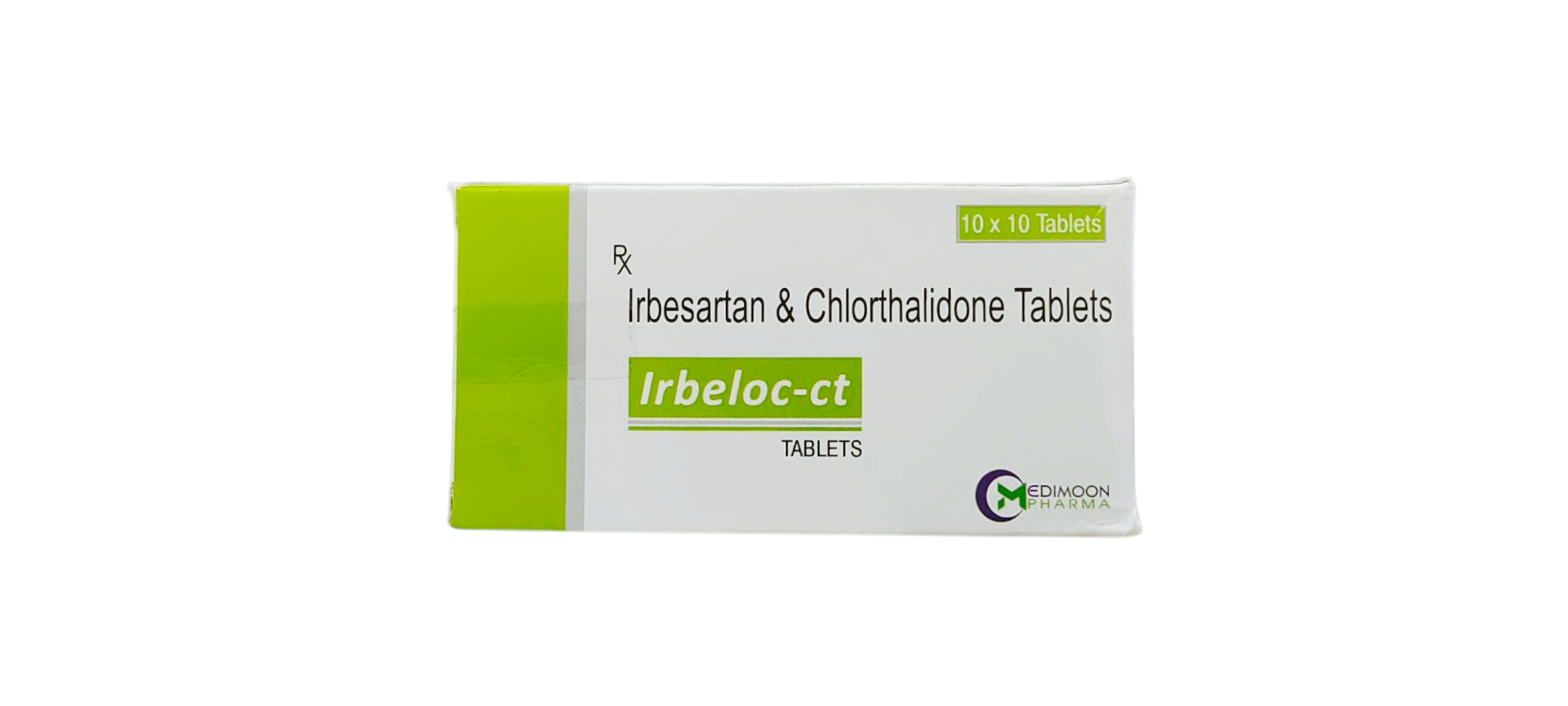
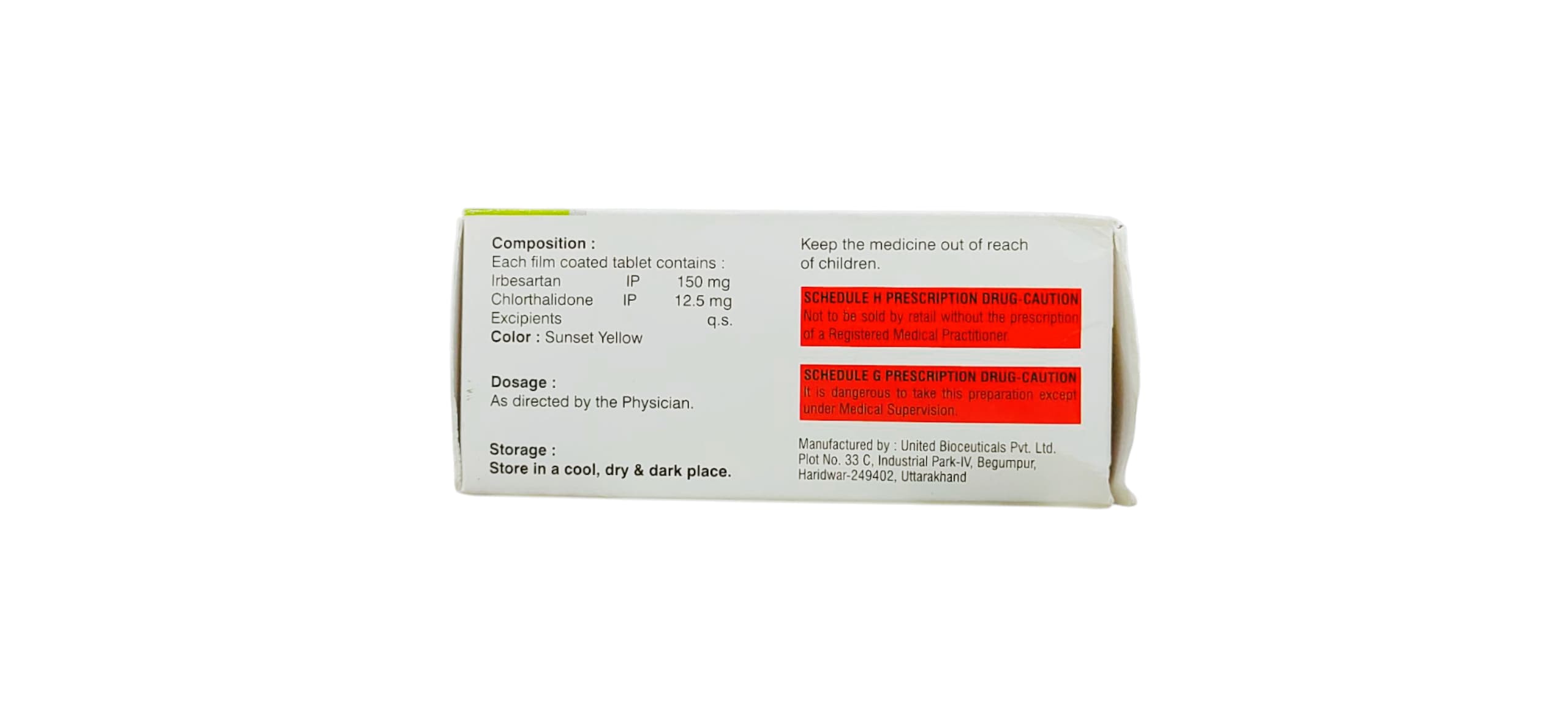
Usage of Irbeloc CT
-
Management of essential hypertension, especially in patients not controlled with monotherapy
-
First-line therapy in patients with:
-
High cardiovascular risk
-
Obesity
-
Diabetic nephropathy or proteinuria
-
Elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension
-
-
Useful in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy
Common Side Effects
-
Irbesartan-related:
-
Dizziness or light-headedness
-
Fatigue
-
Hyperkalemia (rare)
-
GI disturbances (nausea, diarrhea)
-
-
Chlorthalidone-related:
-
Increased urination
-
Electrolyte imbalances (hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia)
-
Gout (hyperuricemia)
-
Hyperglycemia or dyslipidemia (less common at low dose)
-
Precautions
-
Renal impairment: Monitor renal function and serum creatinine, especially in patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis
-
Electrolyte monitoring: Check potassium, sodium, and uric acid periodically
-
Hepatic impairment: Use with caution
-
Avoid in pregnancy – Category D (ARBs can cause fetal harm)
-
Use cautiously in patients on other potassium-sparing agents, NSAIDs, or lithium
Drug Interactions
-
ACE inhibitors or other ARBs: Risk of hyperkalemia and renal impairment
-
NSAIDs: May reduce antihypertensive effect and worsen renal function
-
Potassium supplements / potassium-sparing diuretics: Risk of hyperkalemia
-
Lithium: Toxicity risk increased
-
Antidiabetic drugs: Monitor for altered glucose control with Chlorthalidone
-
Alcohol or sedatives: Additive hypotensive effect
Dosage and Administration
-
Once daily, preferably in the morning to reduce nocturnal diuresis
-
Can be taken with or without food
-
Do not crush or chew the tablet
Storage
-
Store in a cool, dry place below 25°C
-
Protect from light and moisture
Patient Counselling Tips
-
Instruct to take daily at the same time
-
Advise to rise slowly from sitting/lying positions (risk of postural hypotension)
-
Monitor for signs of dehydration, muscle cramps, or palpitations
-
Advise on regular monitoring of BP and lab tests (renal function, electrolytes)
-
Encourage salt restriction and lifestyle changes for optimal BP control
-
Avoid OTC NSAIDs or potassium supplements unless prescribed