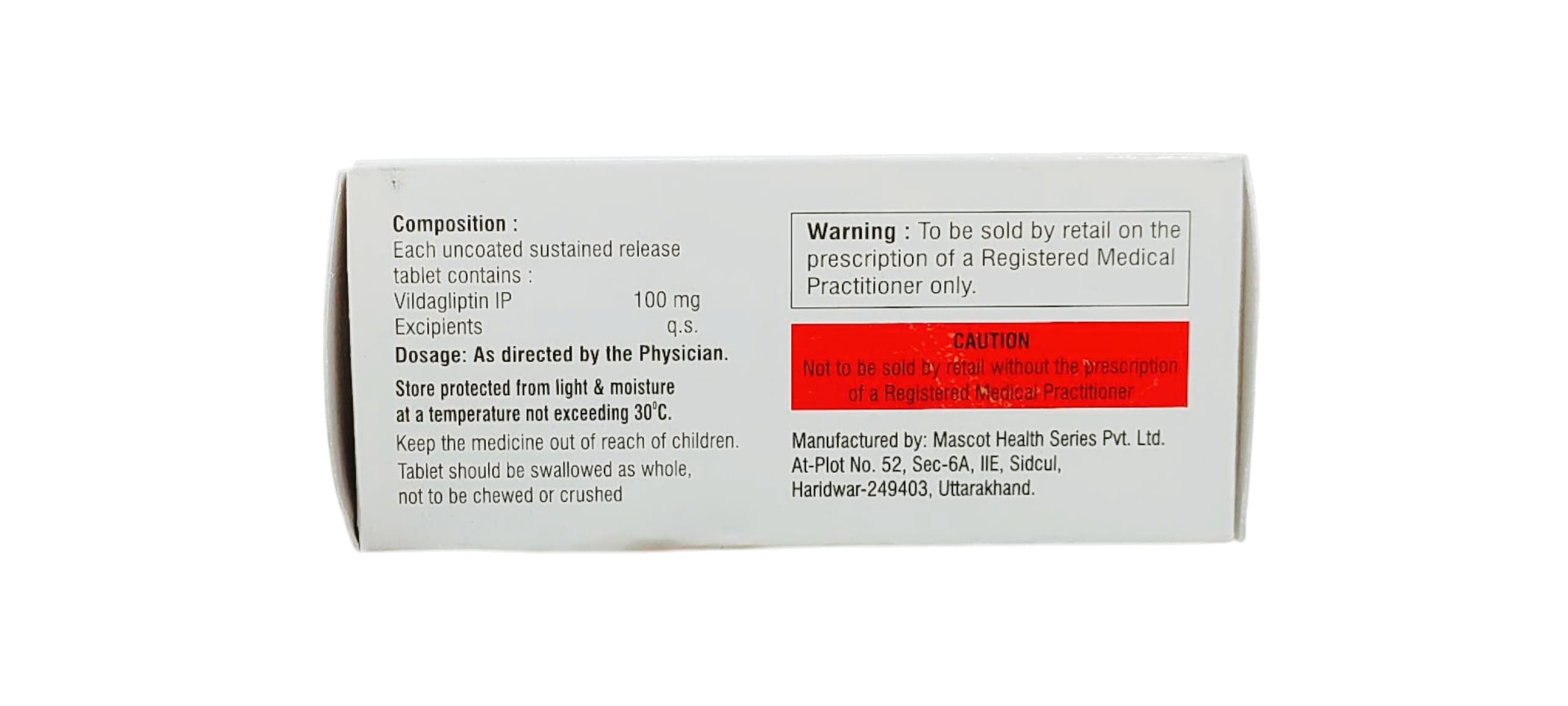
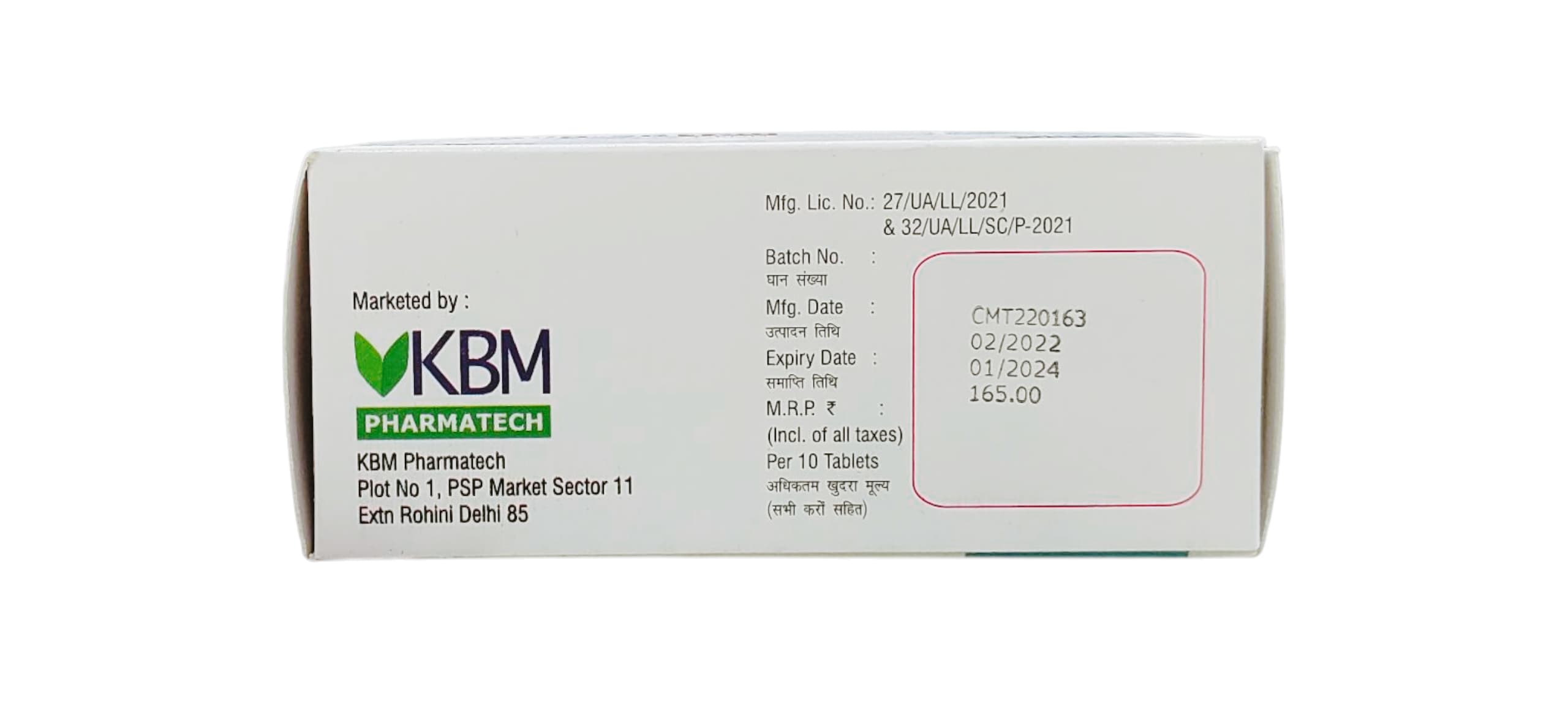
Usage of Medaglip SR 100
Medaglip SR 100 is indicated for:
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (as monotherapy or in combination)
-
Patients inadequately controlled by metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin
-
Diabetics who are elderly, obese, or have renal limitations
-
Preferable for those needing low hypoglycemia risk and weight neutrality
Mechanism of Action
-
Inhibits DPP-4 enzyme, which degrades GLP-1 and GIP (incretins)
-
Increased incretin levels →
🔹 Enhanced insulin secretion in response to meals
🔹 Suppressed glucagon secretion
🔹 Reduced hepatic glucose output -
Results in postprandial and fasting glucose reduction
Key Benefits
✅ Effective HbA1c reduction (~0.7–1.0%)
✅ Weight-neutral
✅ Minimal risk of hypoglycemia
✅ Convenient once-daily sustained release dosing
✅ Safe in elderly and renal-compromised patients (with dose adjustments)
Common Side Effects
-
Headache
-
Dizziness
-
Nausea or constipation
-
Mild peripheral edema (rare)
-
Transient increase in liver enzymes (monitoring recommended)
Precautions
-
Not recommended in Type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
-
Use with caution in patients with hepatic impairment
-
Monitor liver function tests (LFTs) periodically
-
Adjust dose in renal impairment (especially if eGFR < 60 ml/min)
Drug Interactions
-
Generally well tolerated in combination therapy
-
Can be used with:
🔹 Metformin
🔹 Sulfonylureas (monitor for hypoglycemia)
🔹 Thiazolidinediones
🔹 Insulin -
Does not induce or inhibit CYP enzymes significantly
Dosage and Administration
-
One tablet daily, preferably with breakfast
-
May be used as monotherapy or add-on therapy
-
In renal impairment:
-
eGFR 50–80 mL/min: Use 50 mg once daily
-
eGFR < 50 mL/min: Not recommended or use cautiously under monitoring
-
Storage
-
Store below 25°C, protected from light and moisture
-
Keep out of reach of children
Patient Counseling Points
-
Take at the same time every day
-
Report symptoms such as jaundice, fatigue, or upper abdominal pain (possible liver issues)
-
Inform the doctor about any other medications or supplements
-
Continue regular exercise and dietary control
-
Routine blood sugar and LFT monitoring is essential