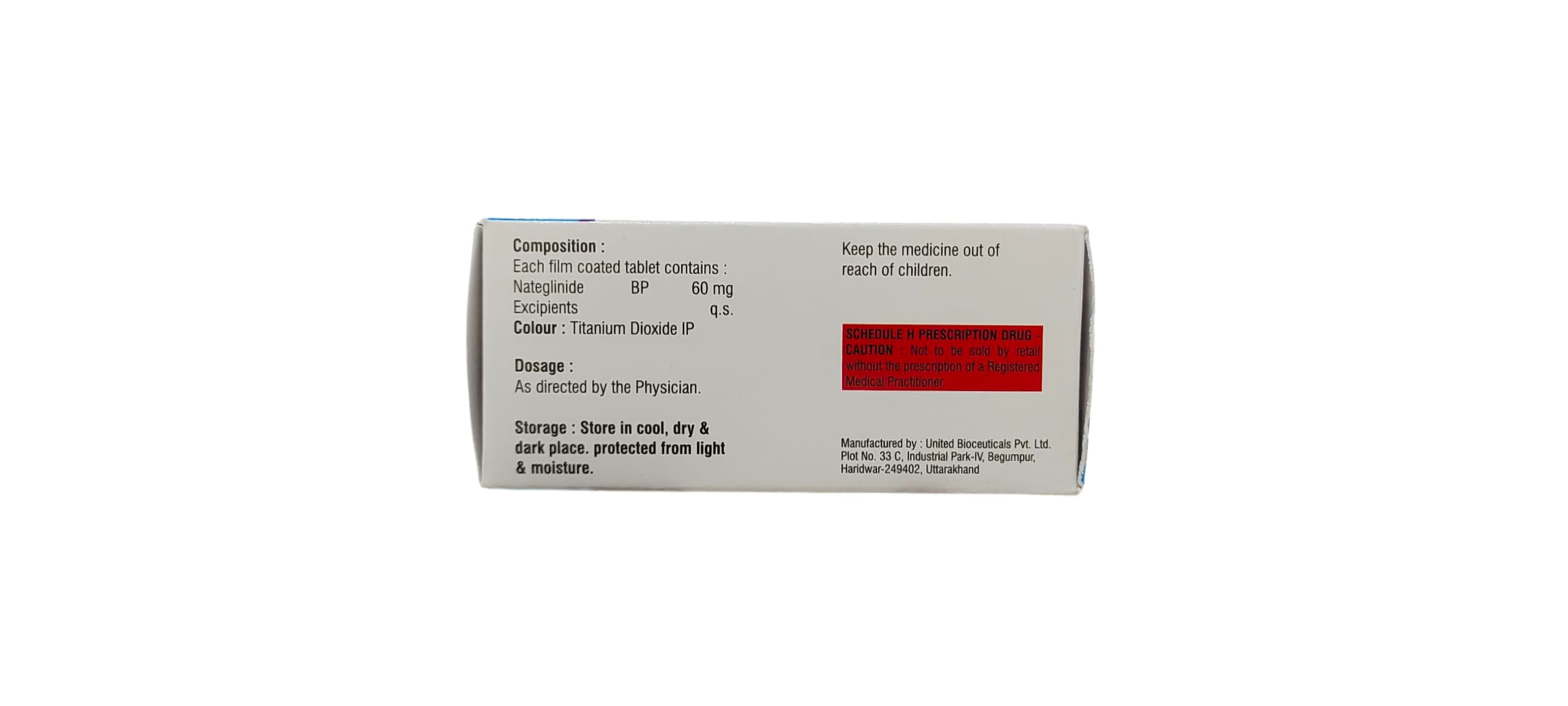
Usage of Nitamoon 60
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
-
As monotherapy in early or mild cases
-
As add-on to metformin in patients with predominant postprandial hyperglycemia
-
In elderly patients or those at risk of hypoglycemia
-
Useful for patients with flexible mealtime habits
-
Can be an alternative to sulfonylureas in patients who need shorter-acting agents
-
Mechanism of Action
Nateglinide closes ATP-dependent potassium channels in pancreatic β-cells, leading to depolarization and calcium influx, which stimulates insulin secretion.
Unlike sulfonylureas, it mimics first-phase insulin response and is glucose-dependent, thereby reducing hypoglycemia risk.
Common Side Effects
-
Mild hypoglycemia (less than sulfonylureas)
-
Upper respiratory tract infections
-
Headache
-
Dizziness
-
Gastrointestinal discomfort (rare)
Most side effects are mild and transient.
Precautions
-
Use caution in patients with hepatic impairment (dose adjustment may be needed)
-
Not recommended in Type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis
-
Avoid in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min)
-
Ensure regular meal timing to avoid hypoglycemia
-
Use with caution in elderly patients
Drug Interactions
-
Beta-blockers: May mask symptoms of hypoglycemia
-
Gemfibrozil: Can increase plasma levels of Nateglinide
-
NSAIDs, salicylates, MAOIs: May potentiate hypoglycemia
-
Diuretics, corticosteroids, thyroid products: May counteract hypoglycemic effects
-
Avoid with sulfonylureas or insulin unless closely monitored
Dosage and Administration
-
60 mg or 120 mg before each major meal
-
Dose depends on glycemic response and HbA1c level
-
Take 1–30 minutes before meals to synchronize with food-induced glucose spikes
-
If a meal is skipped, skip the dose
Storage
-
Store below 25°C, away from light and moisture
-
Keep out of reach of children
Patient Counselling Tips
-
Take just before meals—not after or too early
-
Do not skip meals after taking the dose
-
Report signs of hypoglycemia: sweating, palpitations, shakiness
-
Regular blood sugar monitoring is important
-
Inform your physician about all other medications
Positioning Advantage
-
Faster onset and shorter duration than sulfonylureas
-
Ideal for early diabetes with meal-related glucose spikes
-
Lower risk of sustained hypoglycemia
-
Useful in elderly, busy professionals, or patients with variable meal times